 Light emitting diodes, commonly called LEDs, are real unsung heroes in the electronics world. They do many different jobs in all kinds of devices. They form numbers on digital clocks, transmit information from remote controls, light up watches and tell you when your appliances are turned on.
Light emitting diodes, commonly called LEDs, are real unsung heroes in the electronics world. They do many different jobs in all kinds of devices. They form numbers on digital clocks, transmit information from remote controls, light up watches and tell you when your appliances are turned on. Parts of a conventional LED. The flat bottom surfaces of the anvil and post embedded inside the epoxy act as anchors, to prevent the conductors from being forcefully pulled out via mechanical strain or vibration. Close-up image of a surface-mount LED Close-up of an LED with the voltage being increased and decreased to show a detailed view of its operation A bulb-shaped modern retrofit LED lamp ...
Parts of a conventional LED. The flat bottom surfaces of the anvil and post embedded inside the epoxy act as anchors, to prevent the conductors from being forcefully pulled out via mechanical strain or vibration. Close-up image of a surface-mount LED Close-up of an LED with the voltage being increased and decreased to show a detailed view of its operation A bulb-shaped modern retrofit LED lamp ... How an LED works: When forward biased, electrons and holes in an LED recombine at the depletion layer, releasing energy as light, illustrating how an LED works.
How an LED works: When forward biased, electrons and holes in an LED recombine at the depletion layer, releasing energy as light, illustrating how an LED works.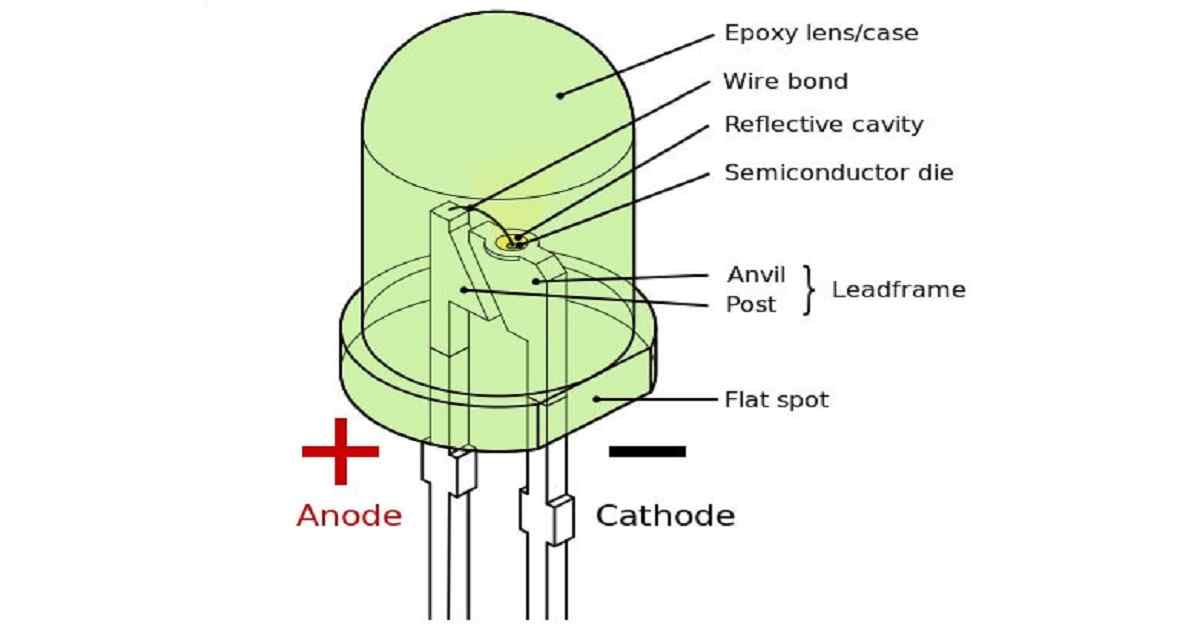 Before we answer the question what is an LED or delve into how LEDs work, let’s do a quick history lesson on a few common types of light emitting devices you’re probably familiar with. After that, we’ll talk about what LEDs are made of and how they work.
Before we answer the question what is an LED or delve into how LEDs work, let’s do a quick history lesson on a few common types of light emitting devices you’re probably familiar with. After that, we’ll talk about what LEDs are made of and how they work.